1 Welcome to the heat sink computation toolbox
Heat sink dimensioning based on analytical calculation of thermal resistance.
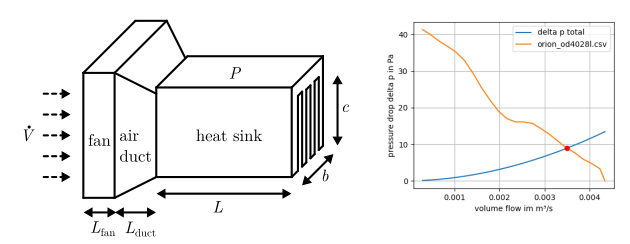
The pressure loss through the cooling system is determined by the specified geometry and the fan. This allows the volume flow rate to be determined. The volume flow can then be used to determine the thermal resistance.
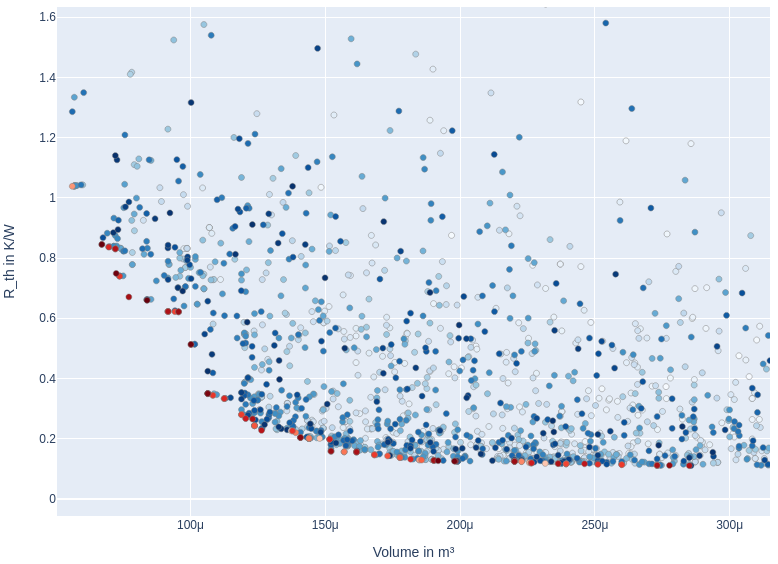
The estimate of the geometry parameters and the fan is mapped to the costs (volume, R_th) using Pareto optimization. About 40 fan characteristic curves are stored in the toolbox.
1.1 Installation
Install in developer mode.
git clone git@github.com:upb-lea/HCT_heat_sink_computation_toolbox.git cd HCT_heat_sink_computation_toolbox/ pip install -e .
1.2 Usage and examples
Check out the examples in this directory.
1.3 Literature
This toolbox implements the thermal basics according to the following paper:
Christoph Gammeter, Florian Krismer and Johann W. Kolar Weight Optimization of a Cooling System Composed of Fan and Extruded Fin Heat Sink
Heat spreading is implemented according to the following Ph.D. thesis:
Christoph Gammeter Multi-Objective Optimization of Power Electronics and Generators of Airborne Wind Turbines
This is supplemented by various calculations and optimizations. E.g. a Pareto optimization is added.
1.4 Bug reports
Please use the issues report button within GitHub to report bugs.
1.5 Contributing
Pull requests are welcome. For major changes, please open an issue first to discuss what you would like to change.
1.6 Changelog
Find the changelog here.
2 Heat Sink Computation Toolbox (HCT) Function Documentation
Plot settings: Normal font or LaTeX font.
- hct.generalplotsettings.colors() dict
Colors according to the GNOME color scheme (Color 4).
- hct.generalplotsettings.global_plot_settings_font_latex() None
Set the plot fonts to LaTeX-font.
- hct.generalplotsettings.global_plot_settings_font_sansserif() None
Set the plot fonts to Sans-Serif-Font.
- hct.generalplotsettings.global_plot_settings_font_size(font_size: float) None
Change the plot font size.
- Parameters:
font_size (float) – font size
Heat spreading calculation according to doctor thesis.
Christoph Gammeter Multi-Objective Optimization of Power Electronics and Generators of Airborne Wind Turbines
- hct.heat_spreading.calc_biot_number(heat_spreading_material: SpreadingMaterial, r_th_zero: float) float
Calculate the biot number.
- Parameters:
heat_spreading_material – heat spreading material
r_th_zero – thermal resistance for the rest of the system (cooling fins)
- hct.heat_spreading.calc_dimensionless_constriction_resistance_psi(epsilon_spreading_material: float, phi_c: float) float
Calculate the dimensionless constriction resistance.
- Parameters:
epsilon_spreading_material – dimensionless geometry factor of the heat sink
phi_c – phi_c according to paper
- hct.heat_spreading.calc_epsilon_spreading_material(heat_spreading_material: SpreadingMaterial) float
Calculate the dimensional factor for the heat spreading material.
- Parameters:
heat_spreading_material – SpreadingMaterial
- hct.heat_spreading.calc_phi_c(tau: float, sigma_c: float, biot_number: float) float
Calculate phi_c.
- Parameters:
tau – tau
sigma_c – sigma_c
biot_number – biot number
- hct.heat_spreading.calc_r_th_m(heat_spreading_material: SpreadingMaterial) float
Calculate the R_th,d (heat sink, baseplate).
- Parameters:
heat_spreading_material (SpreadingMaterial) – heat spreading material according to SpreadingMaterial class
- Returns:
r_th_d in K/W
- hct.heat_spreading.calc_r_th_sp(spreading_material: SpreadingMaterial, r_th_zero: float) float
Calculate the r_th_sp for the spreading material.
- Parameters:
spreading_material – SpreadingMaterial
r_th_zero – r_th_zero, according to the paper, the rest of the heat sink.
- hct.heat_spreading.calc_sigma_c(epsilon_spreading_material: float) float
Calculate the sigma_c factor.
- Parameters:
epsilon_spreading_material – Epsilon for the spreading material
- hct.heat_spreading.calc_spreading_resistance_r_f(heat_spreading_material: SpreadingMaterial, psi: float)
Calculate the spreading resistance r_f.
- Parameters:
psi – dimensionless constriction resistance
heat_spreading_material – SpreadingMaterial
- hct.heat_spreading.calc_tau(heat_spreading_material: SpreadingMaterial) float
Calculate the tau factor.
- Parameters:
heat_spreading_material – SpreadingMaterial
- hct.heat_spreading.verify_with_phd_thesis_gammeter() None
Verify with figure 3.18 (page 149), Ph.D. thesis Gammeter.
Implementation of the hydrodynamic model according to a given paper.
Christoph Gammeter, Florian Krismer, Johann Kolar: ‘Weight Optimization of a Cooling System Composed of Fan and Extruded Fin Heat Sink’
- hct.hydrodynamic.calc_delta_p_acc(geometry: Geometry, volume_flow_v_dot: float, constants: Constants)
Calculate the pressure drop for the frictionless fluid flow acceleration.
- Parameters:
geometry – geometry of the heat sink
volume_flow_v_dot – volume flow in m³/s
constants – constants
- Returns:
pressure drop in Pascal (Pa)
- hct.hydrodynamic.calc_delta_p_duct(f_app_duct: float, l_duct: float, mean_d_h_duct: float, constants: Constants, mean_u_duct: float)
Calculate the duct static pressure drop.
- Parameters:
f_app_duct (float) – apparent friction factor for viscous fluid flow in the air duct
l_duct (float) – length of the air duct
mean_u_duct (float) – average velocity inside the heat sink
mean_d_h_duct (float) – average velocity inside the air duct
constants (Constants) – constants according to the Constants class
- Returns:
pressure difference of the air duct in Pascal (Pa)
- hct.hydrodynamic.calc_delta_p_heat_sink(f_app: float, k_se: float, k_sc: float, constants: Constants, geometry: Geometry, d_h: float, mean_u_hs: float) float
Calculate the pressure drop of the heat sink.
- Parameters:
f_app (float) – apparent friction factor for viscous fluid flow in ducts
k_se (float) – friction factor for sudden contraction
k_sc (float) – friction factor for sudden expansion
constants (Constants) – Constants.
geometry (Geometry) – Geometry.
d_h (float)
mean_u_hs (float) – average velocity inside the heat sink
- Returns:
delta_p_heat_sink in Pascal (Pa).
- Return type:
float
- hct.hydrodynamic.calc_epsilon_duct(geometry: Geometry)
Calculate the epsilon shape factor from the air duct geometry.
- Parameters:
geometry – Geometry parameters
- Returns:
Epsilon shape factor for the air duct.
- hct.hydrodynamic.calc_f_app(geometry: Geometry, constants: Constants, volume_flow_v_dot: float, f_re_sqrt_a: float)
Calculate the apparent friction factor for the average duct hydraulic parameter.
- Parameters:
geometry – Geometry.
constants – Constants.
volume_flow_v_dot – volume flow in m³/s
f_re_sqrt_a
- Returns:
Apparent friction factor for the average duct hydraulic parameter.
- hct.hydrodynamic.calc_f_app_duct(constants: Constants, geometry: Geometry, volume_flow_v_dot: float, f_re_sqrt_a_fd: float)
Calculate the apparent friction factor for the average duct hydraulic diameter.
- hct.hydrodynamic.calc_k_sc(geometry: Geometry)
Calculate the friction factor sudden expansion.
- Parameters:
geometry – Geometry.
- Returns:
Friction factor sudden expansion.
- hct.hydrodynamic.calc_k_se(geometry: Geometry)
Calculate the friction factor for sudden contraction.
- Parameters:
geometry – Geometry
- Returns:
friction factor for sudden contraction.
- hct.hydrodynamic.calc_l_duct(geometry: Geometry)
Calculate the length of the air duct.
- Parameters:
geometry – Geometry
- Returns:
Length of the air duct.
- hct.hydrodynamic.calc_mean_d_h_duct(geometry: Geometry)
Calculate the mean average velocity inside the air duct.
- Parameters:
geometry – Geometry
- Returns:
mean average velocity inside the air duct.
- hct.hydrodynamic.calc_mean_u_duct(geometry: Geometry, volume_flow_v_dot: float)
Calculate the average velocity inside the air duct.
- Parameters:
geometry – Geometry of the heat sink
volume_flow_v_dot – volume flow in m³/s
- Returns:
average velocity inside the air duct in m/s.
- hct.hydrodynamic.calc_mean_u_hs(geometry: Geometry, volume_flow_v_dot: float)
Calculate the average velocity inside the heat sink.
- Parameters:
geometry – Geometry of the heat sink
volume_flow_v_dot – volume flow in m³/s
- Returns:
average velocity inside the heat sink in m/s.
- hct.hydrodynamic.calc_volume_flow(fan_name: str, geometry: Geometry, plot: bool = False, figure_size: tuple | None = None)
Calculate the volume flow for a given fan and a given geometry.
This function calculates the intersection of both graphs, the fan graph and the heat sink pressure graph and returns the intersection point.
- Parameters:
fan_name (str) – file name including .csv ending
geometry (Geometry) – Geometry.
plot (bool) – True to show a visual output.
figure_size (tuple) – Figure size in mm, e.g. (80, 60) is a 80 mm wide and 60 mm height plot
- Returns:
intersection_volume_flow, intersection_pressure
- hct.hydrodynamic.calculate_intersection(x_list: ndarray, y1_list: ndarray, y2_list: ndarray) ndarray
Calculate the intersection between two graphs (x_list, y1_list) and (x_list, y2_list).
The return are both lists (x_list, y1_list) and (x_list, y2_list) added by the intersection points as well as the intersection point itself. :param x_list: common x-coordinates of the two graphs :type x_list: np.ndarray :param y1_list: y-coordinates of graph 1 :type y1_list: np.ndarray :param y2_list: y-coordinates of graph 2 :type y2_list: np.ndarray :return: x_list, y1_list, y2_list (lists are complemented by the intersection point), x_intersection, y_intersection
- hct.hydrodynamic.compare_fan_data() None
Plot all available fan data for comparison.
- hct.hydrodynamic.read_fan_data(filepath: str)
Read stored .csv fan data, translate curves with SI-unit outputs.
- Parameters:
filepath – Filepath to fan .csv-file.
- Returns:
fan_cubic_meter_second, fan_pressure_drop_pascal
Heat sink system optimization using optuna.
- class hct.optimization.Optimization
Optuna optimization for heat sink and fan optimization.
- static df_plot_pareto_front(df: DataFrame, figure_size: tuple) None
Plot an interactive Pareto diagram (losses vs. volume) to select the transformers to re-simulate.
- Parameters:
df (pd.DataFrame) – DataFrame, generated from an optuna study (exported by optuna)
figure_size (tuple) – figures size as a x/y-tuple in mm, e.g. (160, 80)
- static load_config(config_pickle_filepath: str) OptimizationParameters
Load pickle configuration file from disk.
- Parameters:
config_pickle_filepath (str) – filepath to the pickle configuration file
- Returns:
Configuration file as OptimizationParameters object
- Return type:
- static objective(trial: Trial, config: OptimizationParameters) tuple
Objective for the optimization with optuna.
- Parameters:
trial (optuna.Trial) – optuna input suggestions
config (OptimizationParameters) – optimization configuration according to OptimizationParameters class
- Returns:
total_volume, r_th_sa in case of success, nan,nan in case of unrealistic geometry parameters
- static save_config(config: OptimizationParameters) None
Save the configuration file as pickle file on the disk.
- Parameters:
config (OptimizationParameters) – configuration
- static start_proceed_study(config: ~hct.thermal_dataclasses.OptimizationParameters, number_trials: int, storage: str = 'sqlite', sampler: ~optuna.samplers._base.BaseSampler = <optuna.samplers._nsgaiii._sampler.NSGAIIISampler object>) None
Proceed a study which is stored as sqlite database.
- Parameters:
number_trials (int) – Number of trials adding to the existing study
storage (str) – storage database, e.g. ‘sqlite’ or ‘mysql’
sampler (optuna.sampler-object) – optuna.samplers.NSGAIISampler() or optuna.samplers.NSGAIIISampler(). Note about the brackets () !! Default: NSGAIII
config (OptimizationParameters) – configuration according to OptimizationParameters class
- static study_to_df(config: OptimizationParameters) DataFrame
Create a Pandas DataFrame from a study.
- Parameters:
config (OptimizationParameters) – configuration
- Returns:
Study results as Pandas DataFrame
- Return type:
pd.DataFrame
Data class definitions.
- class hct.thermal_dataclasses.Constants(c_1: float, c_2: float, c_3: float, c_4: float, gamma: float, rho_air: float, c_air: float, lambda_air: float, fluid_viscosity_air: float, lambda_material: float, rho_material: float, k_venturi: float)
Define constants.
- class hct.thermal_dataclasses.FanData(manufacturer: str, type: str, width_height: float, length: float, weight: float, datasheet: str)
Define fan data.
- class hct.thermal_dataclasses.Geometry(height_c: float, width_b: float, length_l: float, height_d: float, number_fins_n: int, thickness_fin_t: float, fin_distance_s: float, alpha_rad: float, l_duct_min: float)
Define a single heat sink geometry.
l_duct_min: minimum length of the air duct.
- class hct.thermal_dataclasses.OptimizationParameters(heat_sink_study_name: str, heat_sink_optimization_directory: str, height_c_min_max_list: list, width_b_min_max_list: list, length_l_min_max_list: list, height_d_min_max_list: list, number_fins_n_min_max_list: list, thickness_fin_t_min_max_list: list, fan_list: list, t_ambient: float, number_directions: int, area_min: float | None)
Define optimization parameters.
2 directions: Optimize for minimum volume and minimum R_th, 3 directions: Optimize for minimum volume, minimum R_th and minimum surface area A_min.
- class hct.thermal_dataclasses.SpreadingMaterial(lambda_conductivity: float, thickness_d: float, heat_source_area_a_s: float, spreading_material_area_a_sp: float)
Define the heat spreading material.