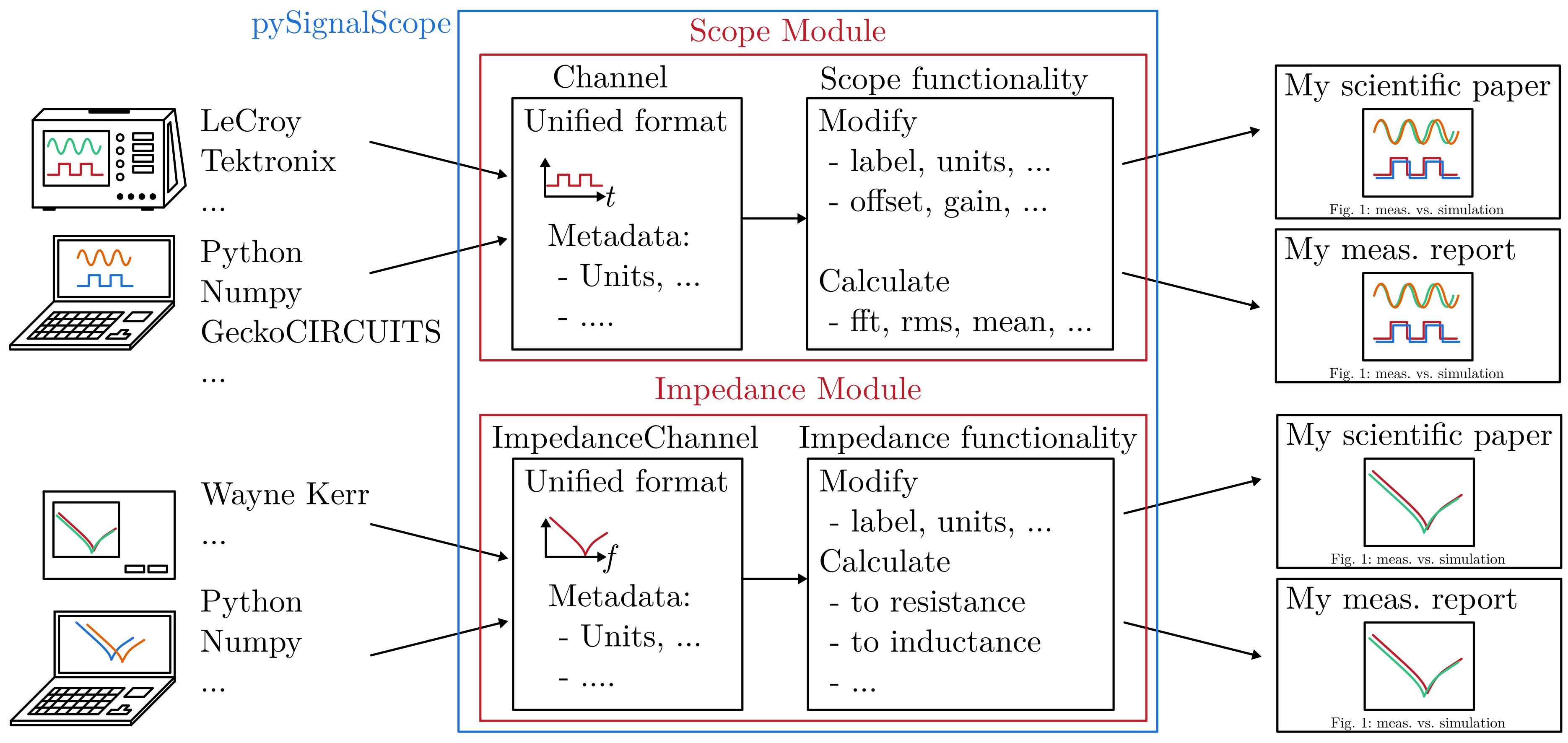
1 Scope toolbox for documentation purposes and comparisons
pySignalScope processes and compares time domain data similar to oscilloscopes in electronics. Signals can be filtered, derived, integrated or evaluated. Furthermore, pySignalScope includes a module for evaluating and editing the impedance curves of an impedance analyzer or comparing them with the simulation. The main purpose is the quick and easy evaluation of signals, as well as the targeted generation of images for technical documentation. Some examples are:
Bachelor / Master / Ph.D. theses,
Scientific papers,
Technical manuals, and
Measurement reports.
1.1 Overview
Bring measurements from the oscilloscope and the circuit simulator into a standardized Channel format.
Edit the signals by using the Scope functionality: shifting them in time (different zero points) or define the zero point for measuring equipment that can only record AC.
Calculate the FFT or important values such as RMS, mean etc.
Bring the originally different input formats into common plots to make comparisons easy.
With the Impedance functionality, ImpedanceChannels can be read in, edited and compared.
A conversion to e.g. the inductance value is possible with just one command.
1.2 Getting started
Install this repository into your virtual environment (venv) or jupyter notebook:
pip install pysignalscope
Use the toolbox in your python program:
import pysignalscope as pss
...
1.3 Example usage
pySignalScope helps to load, edit, display and analyze the signals. The following application example loads a noisy measurement signal, which is first filtered.
import pysignalscope as pss
# Read curves from scope csv file
[voltage_prim, voltage_sec, current_prim, current_sec] = pss.Scope.from_tektronix('scope_example_data_tek.csv')
# Add labels and units to channel: This example considers the Channel 'current_prim' only
current_prim = pss.Scope.modify(current_prim, label='current measured', unit='A', color='red')
# Low pass filter the noisy current signal, modify the Channel attributes label, color and linestyle
current_prim_filtered = pss.Scope.low_pass_filter(current_prim)
current_prim_filtered = pss.Scope.modify(current_prim_filtered, label='current filtered', linestyle='--', color='green')
# Make some modifications on the signal itself: data offset, time offset and factor to the data.
# Short the channel to one period and add label, color and linestyle to the Channel
current_prim_filtered_mod = pss.Scope.modify(current_prim_filtered, data_factor=1.3, data_offset=11, time_shift=2.5e-6)
current_prim_filtered_mod = pss.Scope.short_to_period(current_prim_filtered_mod, f0=200000)
current_prim_filtered_mod = pss.Scope.modify(current_prim_filtered_mod, label='current modified', linestyle='-', color='orange')
# Plot channels, save as pdf
fig1 = pss.Scope.plot_channels([current_prim, current_prim_filtered], [current_prim_filtered_mod], timebase='us')
pss.save_figure(fig1, 'figure.pdf')
# short channels to a single period, perform FFT for current waveforms
current_prim = pss.Scope.short_to_period(current_prim, f0=200000)
current_prim = pss.Scope.modify(current_prim, time_shift=5e-6)
pss.Scope.fft(current_prim)
To simplify the display, colors, linestyle and the label can be attached to the object. This is shown in the plot above.
The lower plot shows the post-processing of the filtered signal. This is multiplied by a small gain, provided with an offset and shortened to a period duration. The label, color and line style are changed. The signals are then plotted with just one plot command.

The functionality for the Impedance module is similar to the Scope module.
In here, ImpedanceChannel objects can be loaded from different sources, which can be a .csv measurement file from an impedance analyzer or a computer generated curve.
ImpedanceChannel objects can be modified in attributes and data, plotted and equivalent circuit parameters can be obtained from measurements.
Have a look at the Scope example and at the Impedance example to see what you can do with this toolbox.
1.4 Naming convention
This toolbox is divided into two modules: The functionality of an oscilloscope (Scope) and the functionality of an impedance analyzer (Impedance).
1.4.1 Scope
The Scope module provides functionalities for editing and evaluating individual channels that are also provided by a real oscilloscope - just on a PC.
Scope creates, imports, edits or evaluates Channels. The following prefixes apply:
generate_: Generates a newChannelno prefix: Is applied to aChanneland results in a newChannel(e.g.add()adds two channels)from_: Generates aChannelfrom an oscilloscope data set, a simulation program or a calculation (e.g.from_tektronixgenerates aChannelfrom a tektronix scope file)calc_: Calculates individual values from aChannel(e.g.calc_rms()calculates the RMS from a givenChannel)plot_: Plots channels in the desired arrangement (e.g.plot_channels()plots the givenChannels)
1.4.2 Impedance
The Impedance module provides functionalities to evaluate impedance curves.
Impedance creates, imports, edits or evaluates ImpedanceChannel.
generate_: Generates a newImpedanceChannelno prefix: Is applied to aImpedanceChanneland results in a newImpedanceChannel(e.g.modify()modifies anImpedanceChannel)from_: Generates aImpedanceChannelfrom an impedance analyzer data set, a simulation program or a calculation (e.g.from_waynekerrgenerates aImpedanceChannelfrom a real measurement file)calc_: Calculates individual values from aImpedanceChannel(e.g.calc_rlc()calculates the equivalent resistance, inductance and capacitance)plot_: PlotsImpedanceChannel(e.g.plot_impedance()plots the givenImpedanceChannels)
1.5 Documentation
Find the documentation here.
1.6 Bug Reports
Please use the issues report button within GitHub to report bugs.
1.7 Changelog
Find the changelog here.
2 pySignalScope function documentation
- class pysignalscope.Channel(time: array, data: array, label: str | None, unit: str | None, color: str | Tuple | None, linestyle: str | None, source: str | None, modulename: str | None)
Dataclass for Channel objects in a special format, to keep labels, units and voltages belonging to a certain curve.
- color: str | Tuple | None
channel color in a plot (optional)
- data: array
data series of the channel (mandatory)
- label: str | None
channel label displayed in a plot (optional)
- linestyle: str | None
channel linestyle in a plot (optional)
- source: str | None
channel source, additional meta data (optional)
- time: array
time series of the channel (mandatory)
- unit: str | None
channel unit displayed in a plot (optional)
- class pysignalscope.Scope
Class to share channel figures (multiple in a scope) in a special format, to keep labels, units and voltages belonging to a certain curve.
- static calc_abs(channel: Channel) Channel
Modify the existing scope channel so that the signal is rectified.
- static calc_absmean(channel: Channel) Any
Calculate the absolute mean of the given channel. Make sure to provide a SINGLE PERIOD of the signal.
- Parameters:
channel (Channel) – Scope channel object
- Returns:
abs(mean(self.data))
- Return type:
Any
- static calc_mean(channel: Channel) Any
Calculate the mean of the given channel. Make sure to provide a SINGLE PERIOD of the signal.
- Parameters:
channel (Channel) – Scope channel object
- Returns:
mean(self.data)
- Return type:
any
- static calc_rms(channel: Channel) Any
Calculate the RMS of a given channel. Make sure to provide a SINGLE PERIOD of the signal.
- Parameters:
channel (Channel) – Scope channel object
- Returns:
rms(self.data).
- Return type:
Any
- static compare_channels(*channels: Channel, shift: List[None | float] | None = None, scale: List[None | float] | None = None, offset: List[None | float] | None = None, timebase: str = 's')
Graphical comparison for datasets. Note: Datasets need to be type Channel.
- Parameters:
channels (Channel) – dataset according to Channel
shift (list[float]) – phase shift in a list for every input dataset (optional parameter)
scale (list[float]) – channel scale factor in a list for every input dataset (optional parameter)
offset (list[float]) – channel offset in a list for every input dataset (optional parameter)
timebase (str) – timebase, can be ‘s’, ‘ms’, ‘us’, ‘ns’ or ‘ps’
- static copy(channel: Channel) Channel
Create a deepcopy of Channel.
- Parameters:
channel (Channel) – Scope channel object
- static derivative(channel: Channel, order: int = 1) Channel
Get the derivative of the data.
In case of measured input signal, it is useful to apply a low-pass filter first.
- static fft(channel: Channel, plot: bool = True)
Perform fft to the signal.
- Parameters:
channel (Channel) – Scope channel object
plot (bool) – True (default) to show a figure (optional parameter)
- Returns:
numpy-array [[frequency-vector],[amplitude-vector],[phase-vector]]
- Return type:
npt.NDArray[list]
- Example:
>>> import pysignalscope as pss >>> import numpy as np >>> channel_example = pss.Scope.from_numpy(np.array([[0, 5e-3, 10e-3, 15e-3, 20e-3], [1, -1, 1, -1, 1]]), f0=100000, mode='time') >>> pss.Scope.fft(channel_example)
- static from_geckocircuits(txt_datafile: str, f0: float | None = None) List[Channel]
Convert a gecko simulation file to Channel.
- Parameters:
txt_datafile (str) – path to text file, generated by geckoCIRCUITS
f0 (float) – fundamental frequency (optional parameter)
- Returns:
List of Channels
- Return type:
list[Channel]
- static from_lecroy(*csv_files: str) List[Channel]
Translate LeCroy csv-files to a list of Channel class objects.
Note: insert multiple .csv-files to get a list of all channels
- Parameters:
csv_files (str) – csv-file from tektronix scope
- Returns:
List of Channel objects
- Return type:
List[‘Channel’]
- Example single channel:
>>> import pysignalscope as pss >>> [current_prim] = pss.Scope.from_lecroy('/path/to/lecroy/files/current_prim.csv')
- Example multiple channels channel:
>>> import pysignalscope as pss >>> [current_prim, current_sec] = pss.Scope.from_lecroy('/path/one/current_prim.csv', '/path/two/current_sec.csv')
- static from_lecroy_remote(scope_channel_number: int, ip_address: str, label: str) Channel
Get the data of a LeCroy oscilloscope and return a Channel object with the collected data.
- Parameters:
scope_channel_number (int) – number of the channel
ip_address (str) – ip-address of the oscilloscope
label (str) – label name of channel
- Returns:
Channel object with collected data
- Return type:
‘Channel’
- static from_numpy(period_vector_t_i: ndarray, mode: str = 'rad', f0: float | None = None, label: str | None = None, unit: str | None = None) Channel
Bring a numpy or list array to an instance of Channel.
- Parameters:
period_vector_t_i (npt.ArrayLike) – input vector np.array([time], [signal])
mode (str) – ‘rad’ [default], ‘deg’ or ‘time’
f0 (float) – fundamental frequency in Hz (optional parameter)
label (str) – channel label (optional parameter)
unit (str) – channel unit (optional parameter)
- Example:
>>> import pysignalscope as pss >>> import numpy as np >>> channel = pss.Scope.from_numpy(np.array([[0, 5e-3, 10e-3, 15e-3, 20e-3], [1, -1, 1, -1, 1]]), f0=100000, mode='time')
- static from_tektronix(csv_file: str) List[Channel]
Translate tektronix csv-file to a tuple of Channel.
Note: Returns a tuple with four Channels (Tektronix stores multiple channel data in single .csv-file, this results to return of a tuple containing Channel’s)
- Parameters:
csv_file (str) – csv-file from tektronix scope
- Returns:
tuple of Channel, depending on the channel count stored in the .csv-file
- Return type:
- Example:
>>> import pysignalscope as pss >>> [voltage, current_prim, current_sec] = pss.Scope.from_tektronix('/path/to/tektronix/file/tek0000.csv')
- static from_tektronix_mso58(*csv_files: str) List[Channel]
Translate tektronix csv-files to a list of Channel class objects.
Note: insert multiple .csv-files to get a list of all channels.
- Parameters:
csv_files (str) – csv-file from tektronix scope
- Returns:
List of Channel objects
- Return type:
List[‘Channel’]
- Example single channel:
>>> import pysignalscope as pss >>> [current_prim] = pss.Scope.from_tektronix_mso58('/path/to/lecroy/files/current_prim.csv')
- Example multiple channels channel:
>>> import pysignalscope as pss >>> [current_prim, current_sec] = pss.Scope.from_tektronix_mso58('/path/one/current_prim.csv', '/path/two/current_sec.csv')
- static from_tektronix_mso58_multichannel(csv_file: str) List[Channel]
Translate tektronix csv-files to a list of Channel class objects.
Note: insert multiple .csv-files to get a list of all channels.
- Parameters:
csv_file (str) – csv-file from tektronix scope
- Returns:
List of Channel objects
- Return type:
List[‘Channel’]
- Example multiple channel csv-file:
>>> import pysignalscope as pss >>> [current_prim, current_sec] = pss.Scope.from_tektronix_mso58_multichannel('/path/to/lecroy/files/currents.csv')
- static generate_channel(time: List[float] | ndarray, data: List[float] | ndarray, label: str | None = None, unit: str | None = None, color: str | tuple | None = None, source: str | None = None, linestyle: str | None = None) Channel
Generate a channel object.
- Parameters:
time (List[float] or np.ndarray) – time series
data (List[float] or np.ndarray) – channel data
label (str) – channel label (optional parameter)
unit (str) – channel unit (optional parameter)
color (str or tuple) – channel color (optional parameter)
source (str) – channel source (optional parameter)
linestyle (str) – channel linestyle (optional parameter) e.g.’-’ ‘–’ ‘-.’ ‘:’ see also https://matplotlib.org/stable/gallery/lines_bars_and_markers/linestyles.html
- static integrate(channel: Channel, label: str | None = None) Channel
Integrate a channels signal.
The default use-case is calculating energy loss (variable naming is for the use case to calculate switch energy from power loss curve, e.g. from double-pulse measurement)
- static load(filepath: str) Channel
Load a Channel file from the hard disk.
- Parameters:
filepath (str) – filepath
- Returns:
loaded Channel object
- Return type:
- static low_pass_filter(channel: Channel, order: int = 1, angular_frequency_rad: float = 0.05) Channel
Implement a butterworth filter on the given signal.
See also: https://docs.scipy.org/doc/scipy/reference/generated/scipy.signal.lfilter.html
- Parameters:
channel (Channel) – Channel object
order (int) – filter order with default = 1 (optional parameter)
angular_frequency_rad (float) – angular frequency in rad. Valid for values 0…1. (optional parameter) with default = 0.05. Smaller value means lower filter frequency.
- Returns:
Channel object with filtered data
- Return type:
- static modify(channel: Channel, data_factor: float | None = None, data_offset: float | None = None, label: str | None = None, unit: str | None = None, color: str | tuple | None = None, source: str | None = None, time_shift: float | None = None, time_shift_rotate: float | None = None, time_cut_min: float | None = None, time_cut_max: float | None = None, linestyle: str | None = None) Channel
Modify channel data like metadata or add a factor or offset to channel data.
Useful for classes with time/data, but without labels or units.
- Parameters:
channel (Channel) – Scope channel object
data_factor (float) – multiply self.data by data_factor (optional parameter)
data_offset (float) – add an offset to self.data (optional parameter)
label (str) – label to add to the Channel-class (optional parameter)
unit (str) – unit to add to the Channel-class (optional parameter)
color (str or tuple) – Color of a channel (optional parameter)
source (str) – Source of a channel, e.g. ‘GeckoCIRCUITS’, ‘Numpy’, ‘Tektronix-Scope’, … (optional parameter)
time_shift (float) – add time to the time base (optional parameter)
time_shift_rotate (float) – shifts a signal by the given time, but the end of the signal will come to the beginning of the signal. Only recommended for periodic signals! (optional parameter)
time_cut_min (float) – removes all time units smaller than the given one (optional parameter)
time_cut_max (float) – removes all time units bigger than the given one (optional parameter)
linestyle (str) – channel linestyle (optional parameter) for details see parameter description of method ‘generate_channel’
- Returns:
Channel object
- Return type:
- static multiply(channel_1: Channel, channel_2: Channel, label: str | None = None) Channel
Multiply two datasets, e.g. to calculate the power from voltage and current.
- static plot_channels(*channel: List[Channel], timebase: str = 's', figure_size: Tuple | None = None, figure_directory: str | None = None) figure
Plot channel datasets.
- Examples:
>>> import pysignalscope as pss >>> ch1, ch2, ch3, ch4 = pss.Scope.from_tektronix('tektronix_csv_file.csv') >>> pss.Scope.plot_channels([ch1, ch2, ch3],[ch4])
Plots two subplots. First one has ch1, ch2, ch3, second one has ch4.
Y-axis labels are set according to the unit, presented in the last curve for the subplot. For own axis labeling, use as unit for the last channel your label, e.g. r”$i_T$ in A”. Note, that the r before the string gives the command to accept LaTeX formulas, like $$.
- Parameters:
channel (list[Channel]) – list of datasets
timebase (str) – timebase, can be ‘s’, ‘ms’, ‘us’, ‘ns’ or ‘ps’
figure_size (Tuple) – None for auto-fit; fig_size for matplotlib (width, length in mm) (optional parameter)
figure_directory (str) – full path with file extension (optional parameter)
- Returns:
Plots
- Return type:
None
- static plot_shiftchannels(channels: List[Channel], shiftstep_x: float | None = None, shiftstep_y: float | None = None, displayrange_x: Tuple[float, float] | None = None, displayrange_y: Tuple[float, float] | None = None) list[float]
Plot channel datasets.
- Examples:
>>> import pysignalscope as pss >>> ch1, ch2, ch3, ch4 = pss.Scope.from_tektronix('tektronix_csv_file.csv') >>> pss.Scope.plot_shiftchannels([ch1, ch2])
Plots the channels ch1 and ch2. You can zoom into by selecting the zoom area with help of left mouse button. By moving the mouse while pressing the button the area is marked by a red rectangle. If you release the left mouse button the area is marked. By moving the mouse within the area an perform a button press, you confirm and you zoom in the area. If you perform the left mouse button click outside of the marked area, you reject the selection. You reject the selection always by clicking the right mouse button independent you zoom out. button. If no area is selected or wait for confirmation, the click on the right mouse button leads to zooming out. There is a zoom limit in both directions. In this case, the rectangle shows the possible area (becomes larger), after you have release the left mouse button.
Y-axis labels are set according to the unit, presented in the last curve for the subplot. For own axis labeling, use as unit for the last channel your label, e.g. r”$i_T$ in A”. Note, that the r before the string gives the command to accept LaTeX formulas, like $$. The parameters has to fullfill conditions: Minimal shift step in x-direction is the minimal difference of 2 points of all provided channels
- Parameters:
channels (list[Channel]) – list of datasets
shiftstep_x (float) – shift step in x-direction (optional parameter) Has to be in range ‘minimal difference of 2 points of the channels’ to (‘displayed maximal x-value minus displayed minimal x-value’)/10
shiftstep_y (float) – shift step in y-direction (optional parameter) Has to be in range (‘displayed maximal y-value minus displayed minimal y-value’)/200 to (‘displayed maximal y-value minus displayed minimal y-value’)/10
displayrange_x (tuple of float) – Display range limits in x-direction (min_x, max_x) (optional parameter) Definition: delta_min_x = 100 * ‘minimum distance between 2 samples’, min_x = ‘minimal x-value (of all channels)’, max_x = ‘maximal x-value (of all channels)’, delta_x = max_x-min_x The range for displayrange_x[0]: From min_x-delta_x to max_x-delta_min_x The range for displayrange_x[1]: From min_x+delta_min_x to max_x+delta_x and displayrange_x[1]-displayrange_x[0]>=delta_min_x
displayrange_y (tuple of float) – Display range limits in y-direction (min_y, max_y) (optional parameter) Definition: delta_y = max_y-min_y, min_y = ‘minimal y-value (of all channels)’, max_y = ‘maximal y-value (of all channels)’, delta_min_y = delta_y/100 The range for displayrange_y[0]: From min_y-delta_y to max_y-delta_min_y*50 The range for displayrange_y[1]: From min_y+delta_min_y*50 to max_y-delta_y and displayrange_y[1]-displayrange_y[0]>=delta_min_y*50
- Returns:
List of x and y-shifts per channel
- Return type:
list[float]
- static save(channel: Channel, filepath: str) None
Save a Channel object to hard disk.
- Parameters:
channel (Channel) – Channel object
filepath (str) – filepath including file name
- static short_to_period(channel: Channel, f0: float | int | None = None, time_period: float | int | None = None, start_time: float | int | None = None)
Short a given Channel object to a period.
- Parameters:
channel (Channel) – Scope channel object
f0 (float) – frequency in Hz (optional parameter)
time_period (float) – time period in seconds (optional parameter)
start_time (float) – start time in seconds (optional parameter)
- static unify_sampling_rate(*channel_datasets: Channel, sample_calc_mode: str, sampling_rate: float | None = None, shift: float | None = None, mastermode: bool = True) list[Channel]
unifies the sampling rate of datasets.
- Examples:
>>> import pysignalscope as pss >>> ch1 = pss.Scope.generate_channel([-1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10], >>> [-8, -2, 10.5, 11, 13, 14, 16, 20, 17, 14, 9, 1]) >>> ch2 = pss.Scope.generate_channel([-0.5, 0, 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2, 2.5, 3, 3.5, 4, 4.5], >>> [10, 2, 7.5, -2.5, 4, 8, 4, 10, 2, 20, 5]) >>> result_list= pss.Scope.unify_sampling_rate(ch1,ch2,sample_calc_mode="min")
- Parameters:
channel_datasets (Channel) – dataset according to Channel
sample_calc_mode (str) – keyword, which define the sampling rate calculation possible keywords are ‘avg’, ‘max’, ‘min’ ‘user’
sampling_rate (float) – sampling rate defined by the user (optional parameter) only valid, if sample_calc_mode is set to ‘user’
shift (float) – shift of the sample rate from origin (optional parameter) None corresponds to a shift to first time point of first channel
mastermode (bool) – Indicates the channels, which are used for sampling rate calculation (optional parameter) True (default): Only the first channel is used for sampling rate calculation False: All channels are used for sampling rate calculation
- Returns:
List of channels
- Return type:
list[‘Channel’]
If the mastermode is ‘True’ (default), only the first data set is used for sampling rate calculation. This parameter is ignored, if the sample_calc_mode approach is set to ‘user’ For the calculation of the data rate following approaches can be select by parameter ‘sample_calc_mode’: ‘avg’ = Average sampling rate: The sampling rate shall be calculated by the average distance of the sampling rate. ‘max’ = Maximal sampling rate: The sampling rate shall be calculated by the minimum distance between two sample points. ‘min’ = Minimal sampling rate: The sampling rate shall be calculated by the maximal distance between two sample points. ‘user’ = Sampling rate is defined by the user. This selection raises an error, if the parameter ‘sampling_rate’
isn’t a valid float value, which corresponds to the sampling frequency.
- class pysignalscope.ImpedanceChannel(frequency: array, impedance: array, phase_deg: array, label: str | None, unit: str | None, color: str | tuple | None, linestyle: str | None, source: str | None)
Dataclass for ImpedanceChannel objects in a special format, to keep labels, units and voltages belonging to a certain curve.
- color: str | tuple | None
channel color displayed in a plot (optional)
- frequency: array
frequency data (mandatory)
- Type:
mandatory
- impedance: array
impedance data (mandatory)
- Type:
mandatory
- label: str | None
channel label displayed in a plot (optional)
- linestyle: str | None
channel linestyle displayed in a plot (optional)
- phase_deg: array
phase data in degree (mandatory)
- Type:
mandatory
- source: str | None
channel source, additional meta data (optional)
- unit: str | None
channel unit displayed in a plot (optional)
- class pysignalscope.Impedance
Class to share scope figures in a special format, to keep labels, units and voltages belonging to a certain curve.
- static calc_re_im_parts(channel: ImpedanceChannel, show_figure: bool = True)
Calculate real and imaginary part of Impedance measurement.
- Parameters:
channel (ImpedanceChannel) – Impedance object
show_figure (bool) – Plot figure if true
- Returns:
List with [(frequency, frequency_real_part), (frequency, frequency_imag_part)]
- Return type:
List
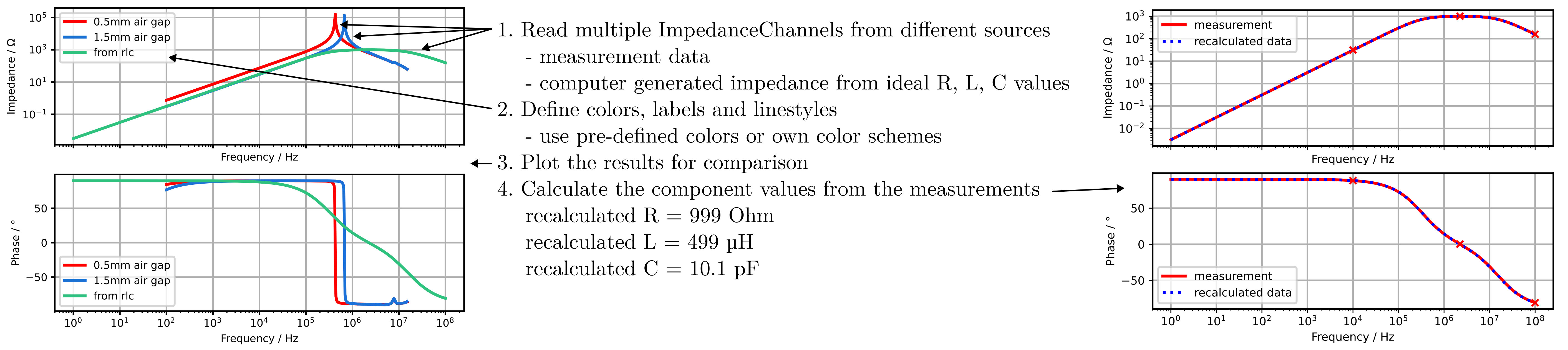
- static calc_rlc(channel: ImpedanceChannel, type_rlc: str, f_calc_c: float, f_calc_l: float, plot_figure: bool = False) tuple
Calculate R, L, C values for given ImpedanceChannel.
Calculated values will be drawn in a plot for comparison with the given data.
- Parameters:
channel (ImpedanceChannel) – Impedance channel object
type_rlc (str) – Type ‘R’, ‘L’, ‘C’
f_calc_c (float) – Choose the frequency for calculation of C-value
f_calc_l (float) – Choose the frequency for calculation of L-value
plot_figure (bool) – True/False [default] to plot the figure
- Returns:
Values for R, L, C
- Return type:
tuple
- Example:
>>> import pysignalscope as pss >>> example_data_rlc = pss.Impedance.from_rlc('l', 1000, 500e-6, 10e-12) >>> recalculated_r, recalculated_l, recalculated_c = pss.Impedance.calc_rlc(example_data_rlc, 'l', f_calc_l=10e3, f_calc_c=10e7, plot_figure=True)
- static check_capacitor_from_waynekerr(csv_filename: str, label: str, target_capacitance: float, plot_figure: bool = True) ImpedanceChannel
Check a capacitor impedance .csv-curve against a target capacitance.
Reads the .csv-curve from wayne kerr impedance analyzer, calculates r, l, and c from the measurement and shows the derivation from the target capacitance. Visualizes the curves in case of plot_figure is set to true.
- Parameters:
csv_filename (str) – filepath to Wayne Kerr impedance analyzer .csv-file
label (str) – channel label for the plot
target_capacitance (float) – target capacitance in F
plot_figure (bool) – Set to True for plot
- Returns:
measured capacitor as impedance curve
- Return type:
- static copy(channel: ImpedanceChannel) ImpedanceChannel
Create a deepcopy of ImpedanceChannel.
- Parameters:
channel (ImpedanceChannel) – Impedance object
- Returns:
Deepcopy of the impedance object
- Return type:
- static from_kemet_ksim(csv_filename: str) ImpedanceChannel
Import data from kemet “ksim” tool.
- Parameters:
csv_filename (str) – path to csv-file
- Returns:
ImpedanceChannel object
- Return type:
- static from_rlc(type_rlc: str, resistance: float | array, inductance: float | array, capacitance: float | array) ImpedanceChannel
Calculate the impedance over frequency for R - L - C - combination.
- Parameters:
type_rlc (str) – Type of network, can be ‘R’, ‘L’ or ‘C’
resistance (float) – resistance
inductance (float) – inductance
capacitance (bool) – capacitance
- Returns:
Impedance object
- Return type:
- Example:
>>> import pysignalscope as pss >>> impedance_channel_object = pss.Impedance.from_rlc('C', 10e-3, 100e-9, 36e-3)
Type C and RLC
---R---L---C---
Type R
---+---R---L---+--- | | +-----C-----+
Type L
---+---L---+--- | | +---C---+ | | +---R---+
- static from_waynekerr(csv_filename: str, label: str | None = None) ImpedanceChannel
Bring csv-data from wayne kerr 6515b to Impedance.
- Parameters:
csv_filename (str) – .csv filename from impedance analyzer
label (str) – label to add to the Channel-class, optional.
- Returns:
ImpedanceChannel object
- Return type:
- static generate_impedance_object(frequency: List | _SupportsArray[dtype[Any]] | _NestedSequence[_SupportsArray[dtype[Any]]] | bool | int | float | complex | str | bytes | _NestedSequence[bool | int | float | complex | str | bytes], impedance: List | _SupportsArray[dtype[Any]] | _NestedSequence[_SupportsArray[dtype[Any]]] | bool | int | float | complex | str | bytes | _NestedSequence[bool | int | float | complex | str | bytes], phase: List | _SupportsArray[dtype[Any]] | _NestedSequence[_SupportsArray[dtype[Any]]] | bool | int | float | complex | str | bytes | _NestedSequence[bool | int | float | complex | str | bytes], label: str | None = None, unit: str | None = None, color: str | tuple | None = None, source: str | None = None, linestyle: str | None = None) ImpedanceChannel
Generate the ImpedanceChannel object.
- Parameters:
frequency (Union[List, npt.ArrayLike]) – channel frequency in Hz
impedance (Union[List, npt.ArrayLike]) – channel impedance in Ohm
phase (Union[List, npt.ArrayLike]) – channel phase in degree
label (str) – channel label to show in plots
unit (str) – channel unit to show in plots
color (str) – channel color
source (str) – Source, e.g. Measurement xy, Device yy
linestyle (str) – line style for the plot e.g. ‘–’
- Returns:
ImpedanceChannel
- Return type:
- static load(filepath: str) ImpedanceChannel
Load an ImpedanceChannel file from the hard disk.
- Parameters:
filepath (str) – filepath
- Returns:
loaded ImpedanceChannel object
- Return type:
- static modify(channel: ImpedanceChannel, impedance_factor: float | None = None, impedance_offset: float | None = None, label: str | None = None, unit: str | None = None, color: str | Tuple | None = None, source: str | None = None, linestyle: str | None = None, frequency_cut_min: float | None = None, frequency_cut_max: float | None = None) ImpedanceChannel
Modify channel data like metadata or add a factor or offset to channel data.
Useful for ImpedanceChannel with frequency/data, but without labels or units.
- Parameters:
channel (ImpedanceChannel) – Impedance object to modify
impedance_factor (float) – multiply channel.impedance by impedance_factor
impedance_offset (float) – add an offset to channel.impedance
label (str) – label to add to the Channel-class
unit (str) – unit to add to the Channel-class
color (str) – Color of a channel
source (str) – Source of a channel, e.g. ‘GeckoCIRCUITS’, ‘Numpy’, ‘Tektronix-Scope’, …
frequency_cut_min (float) – minimum frequency
frequency_cut_max (float) – maximum frequency
linestyle (str) – linestyle of channel, e.g. ‘–’
- Returns:
Modified ImpedanceChannel object
- Return type:
- static plot_component(channel: ImpedanceChannel, figure_size: Tuple | None = None) None
Plot the component values.
Phase must be -90°, 0°, +90° for all entries.
- Parameters:
channel (List) – Impedance
figure_size (Tuple) – figure size as tuple in mm, e.g. (80, 80)
- static plot_impedance(channel_list: List, figure_size: Tuple | None = None) figure
Plot and compare impedance channels.
- Parameters:
channel_list (List) – List with impedances
figure_size (Tuple) – figure size as tuple in mm, e.g. (80, 80)
- Returns:
matplotlib figure
- Return type:
plt.figure
- static plot_inductance_and_ac_resistance(channel_list: List) None
Plot and compare inductance (in uH) and ac_resistance (Ohm) of impedance channels.
- Parameters:
channel_list (List) – List with impedances
- static save(channel: ImpedanceChannel, filepath: str) None
Save an ImpedanceChannel object to hard disk.
- Parameters:
channel (ImpedanceChannel) – impedance channel
filepath (str) – filepath including file name
- static to_capacitance(channel: ImpedanceChannel) ImpedanceChannel
Convert an ImpedanceChannel to a pure capacitance ImpedanceChannel.
Ignore the resistive and inductive part by trigonometric operation.
- Parameters:
channel (ImpedanceChannel) – Impedance channel object
- Returns:
Impedance channel as inductance
- Return type:
- static to_inductance(channel: ImpedanceChannel) ImpedanceChannel
Convert an ImpedanceChannel to a pure inductance ImpedanceChannel.
Ignore the resistive and capacitive part by trigonometric operation.
- Parameters:
channel (ImpedanceChannel) – Impedance channel object
- Returns:
Impedance channel as inductance
- Return type:
- static to_resistance(channel: ImpedanceChannel) ImpedanceChannel
Convert an ImpedanceChannel to a pure resistive ImpedanceChannel.
Ignore the inductive and capacitive part by trigonometric operation.
- Parameters:
channel (ImpedanceChannel) – Impedance channel object
- Returns:
Impedance channel as inductance
- Return type:
Functions uses by the scope, e.g. the fft-function.
- pysignalscope.functions.fft(period_vector_t_i: List[List[float]] | ndarray, sample_factor: int = 1000, plot: bool = True, mode: str = 'rad', f0: float | None = None, title: str = 'ffT', filter_type: str = 'factor', filter_value_factor: float = 0.01, filter_value_harmonic: int = 100, figure_size: Tuple | None = None, figure_directory: str | None = None) List[List]
Calculate the FFT for a given input signal. Input signal is in vector format and should include one period.
Output vector includes only frequencies with amplitudes > 1% of input signal
- Minimal Example:
>>> import pysignalscope as pss >>> import numpy as np >>> example_waveform = np.array([[0, 1.34, 3.14, 4.48, 6.28],[-175.69, 103.47, 175.69, -103.47,-175.69]]) >>> out = pss.fft(example_waveform, plot=True, mode='rad', f0=25000, title='ffT input current')
- Parameters:
period_vector_t_i (np.array or List[List[float]) – numpy-array [[time-vector[,[current-vector]]. One period only
sample_factor (int) – f_sampling/f_period with default = 1000 (optional parameter)
plot (str) – insert anything else than “no” or ‘False’ to show a plot to visualize input and output (optional parameter)
mode (str) – ‘rad’[default]: full period is 2*pi, ‘deg’: full period is 360°, ‘time’: time domain. (optional parameter)
f0 (float) – fundamental frequency. Needs to be set in ‘rad’- or ‘deg’-modewith (optional parameter)
title (str) – plot window title, defaults to ‘ffT’ (optional parameter)
filter_type (str) – ‘factor’[default] or ‘harmonic’ or ‘disabled’. (optional parameter)
filter_value_factor (float) – filters out amplitude-values below a certain factor of max. input amplitude. (optional parameter) Should be 0…1, default to 0.01 (1%)
filter_value_harmonic (int) – filters out harmonics up to a certain number with default = 100 (optional parameter) Note: count 1 is DC component, count 2 is the fundamental frequency
figure_size (Tuple) – None for auto-fit; fig_size for matplotlib (width, length) (optional parameter)
figure_directory (Tuple) – full path with file extension (optional parameter)
- Returns:
numpy-array [[frequency-vector],[amplitude-vector],[phase-vector]]
- Return type:
npt.NDArray[list]
- pysignalscope.functions.save_figure(figure: figure, fig_name: str)
Save the given figure object as pdf.
- Parameters:
figure (matplotlib.pyplot.figure) – figure object
fig_name (str) – figure name for pdf file naming
Set general plot settings, like LaTeX font.
- pysignalscope.generalplotsettings.global_plot_settings_font_latex()
Set the plot fonts to LaTeX-font.
- pysignalscope.generalplotsettings.global_plot_settings_font_sansserif()
Set the plot fonts to Sans-Serif-Font.
- pysignalscope.generalplotsettings.global_plot_settings_unit_delimiter_in() None
Set the plot labeling delimiter to “in”.
e.g. Voltage in V
- pysignalscope.generalplotsettings.global_plot_settings_unit_delimiter_slash() None
Set the plot labeling delimiter to “/”.
e.g. Voltage / V
- pysignalscope.generalplotsettings.update_font_size(font_size: int = 11)
Update the figure font size.
- Parameters:
font_size (int) – font sitze
Definitions for different color schemes.