Electric Motors
Electric Motor Base Class
- class gym_electric_motor.physical_systems.electric_motors.ElectricMotor(motor_parameter=None, nominal_values=None, limit_values=None, motor_initializer=None, initial_limits=None)[source]
Base class for all technical electrical motor models.
A motor consists of the ode-state. These are the dynamic quantities of its ODE. For example:
- ODE-State of a DC-shunt motor: `` [i_a, i_e ] ``
i_a: Anchor circuit current
i_e: Exciting circuit current
Each electric motor can be parametrized by a dictionary of motor parameters, the nominal state dictionary and the limit dictionary.
Initialization is given by initializer(dict). It can be constant state value or random value in given interval. dict should be like: { ‘states’(dict): with state names and initital values
- ‘interval’(array like): boundaries for each state
(only for random init), shape(num states, 2)
‘random_init’(str): ‘uniform’ or ‘normal’ ‘random_params(tuple): mue(float), sigma(int)
- Example initializer(dict) for constant initialization:
{ ‘states’: {‘omega’: 16.0}}
- Example initializer(dict) for random initialization:
{ ‘random_init’: ‘normal’}
- Parameters:
motor_parameter – Motor parameter dictionary. Contents specified for each motor.
nominal_values – Nominal values for the motor quantities.
limit_values – Limits for the motor quantities.
motor_initializer –
Initial motor states (currents) (‘constant’, ‘uniform’, ‘gaussian’ sampled from
given interval or out of nominal motor values)
initial_limits – limits for of the initial state-value
- CURRENTS = []
List of the motor currents names
- Type:
CURRENTS(list(str))
- CURRENTS_IDX = []
Indices for accessing all motor currents.
- Type:
CURRENTS_IDX(list(int))
- HAS_JACOBIAN = False
Parameter indicating if the class is implementing the optional jacobian function
- VOLTAGES = []
List of the motor input voltages names
- Type:
VOLTAGES(list(str))
- electrical_jacobian(state, u_in, omega, *_)[source]
Calculation of the jacobian of each motor ODE for the given inputs / The motors ODE-System.
Overriding this method is optional for each subclass. If it is overridden, the parameter HAS_JACOBIAN must also be set to True. Otherwise, the jacobian will not be called.
- Parameters:
state (ndarray(float)) – The motors state.
u_in (list(float)) – The motors input voltages.
omega (float) – Angular velocity of the motor
- Returns:
[0]: Derivatives of all electrical motor states over all electrical motor states shape:(states x states) [1]: Derivatives of all electrical motor states over omega shape:(states,) [2]: Derivative of Torque over all motor states shape:(states,)
- Return type:
Tuple(ndarray, ndarray, ndarray)
- electrical_ode(state, u_in, omega, *_)[source]
Calculation of the derivatives of each motor state variable for the given inputs / The motors ODE-System.
- Parameters:
state (ndarray(float)) – The motors state.
u_in (list(float)) – The motors input voltages.
omega (float) – Angular velocity of the motor
- Returns:
Derivatives of the motors ODE-system for the given inputs.
- Return type:
ndarray(float)
- i_in(state)[source]
- Parameters:
state (ndarray(float)) – ODE state of the motor
- Returns:
List of all currents flowing into the motor.
- Return type:
list(float)
- property initial_limits
Returns: dict: nominal motor limits for choosing initial values
- initialize(state_space, state_positions, **__)[source]
Initializes given state values. Values can be given as a constant or sampled random out of a statistical distribution. Initial value is in range of the nominal values or a given interval. Values are written in initial_states attribute
- Parameters:
state_space (gymnasium.Box) – normalized state space boundaries (given by physical system)
state_positions (dict) – indices of system states (given by physical system)
- property initializer
Returns: dict: Motor initial state and additional initializer parameter
- property limits
Readonly motors limit state array. Entries are set to the maximum physical possible values in case of unspecified limits.
- Returns:
Limits of the motor.
- Return type:
dict(float)
- property motor_parameter
Returns: dict(float): The motors parameter dictionary
- property nominal_values
Readonly motors nominal values.
- Returns:
Current nominal values of the motor.
- Return type:
dict(float)
- reset(state_space, state_positions, **__)[source]
Reset the motors state to a new initial state. (Default 0)
- Parameters:
state_space (gymnasium.Box) – normalized state space boundaries
state_positions (dict) – indexes of system states
- Returns:
The initial motor states.
- Return type:
numpy.ndarray(float)
Synchronous Motors
Parameter Dictionary
Key |
Description |
Default |
|---|---|---|
r_s |
Stator Resistance in Ohm |
4.9 |
l_d |
d-axis inductance in Henry |
79e-3 |
l_q |
q-axis inductance in Henry |
113e-3 |
j_rotor |
Moment of inertia of the rotor |
2.45e-3 |
psi_p |
Permanent linked rotor flux |
0.165 |
p |
Pole pair Number |
2 |
All nominal voltages and currents are peak phase values. Therefore, data sheet values for line voltages and phase currents has to be transformed such that \(U_N=\sqrt(2/3) U_L\) and \(I_N=\sqrt(2) I_S\).
Furthermore, the angular velocity is the electrical one and not the mechanical one \(\omega = p \omega_{me}\).
- class gym_electric_motor.physical_systems.electric_motors.SynchronousMotor(motor_parameter=None, nominal_values=None, limit_values=None, motor_initializer=None)[source]
The SynchronousMotor and its subclasses implement the technical system of a three phase synchronous motor.
This includes the system equations, the motor parameters of the equivalent circuit diagram, as well as limits and bandwidth.
Motor Parameter
Unit
Default Value
Description
r_s
Ohm
0.78
Stator resistance
l_d
H
1.2
Direct axis inductance
l_q
H
6.3e-3
Quadrature axis inductance
psi_p
Wb
0.0094
Effective excitation flux (PMSM only)
p
1
2
Pole pair number
j_rotor
kg/m^2
0.017
Moment of inertia of the rotor
Motor Currents
Unit
Description
i_sd
A
Direct axis current
i_sq
A
Quadrature axis current
i_a
A
Current through line a
i_b
A
Current through line b
i_c
A
Current through line c
i_alpha
A
Current in alpha axis
i_beta
A
Current in beta axis
Motor Voltages
Unit
Description
u_sd
V
Direct axis voltage
u_sq
V
Quadrature axis voltage
u_a
V
Phase voltage for line a
u_b
V
Phase voltage for line b
u_c
V
Phase voltage for line c
u_alpha
V
Phase voltage in alpha axis
u_beta
V
Phase voltage in beta axis
Limits /
Nominal Value Dictionary Entries:
Entry
Description
i
General current limit / nominal value
i_a
Current in phase a
i_b
Current in phase b
i_c
Current in phase c
i_alpha
Current in alpha axis
i_beta
Current in beta axis
i_sd
Current in direct axis
i_sq
Current in quadrature axis
omega
Mechanical angular Velocity
torque
Motor generated torque
epsilon
Electrical rotational angle
u_a
Phase voltage in phase a
u_b
Phase voltage in phase b
u_c
Phase voltage in phase c
u_alpha
Phase voltage in alpha axis
u_beta
Phase voltage in beta axis
u_sd
Phase voltage in direct axis
u_sq
Phase voltage in quadrature axis
Note
The voltage limits should be the peak-to-peak value of the phase voltage (\(\hat{u}_S\)). A phase voltage denotes the potential difference from a line to the neutral point in contrast to the line voltage between two lines. Typically the root mean square (RMS) value for the line voltage (\(U_L\)) is given as \(\hat{u}_S=\sqrt{2/3}~U_L\)
The current limits should be the peak-to-peak value of the phase current (\(\hat{i}_S\)). Typically the RMS value for the phase current (\(I_S\)) is given as \(\hat{i}_S = \sqrt{2}~I_S\)
If not specified, nominal values are equal to their corresponding limit values. Furthermore, if specific limits/nominal values (e.g. i_a) are not specified they are inferred from the general limits/nominal values (e.g. i)
- Parameters:
motor_parameter – Motor parameter dictionary. Contents specified for each motor.
nominal_values – Nominal values for the motor quantities.
limit_values – Limits for the motor quantities.
motor_initializer –
Initial motor states (currents) (‘constant’, ‘uniform’, ‘gaussian’ sampled from
given interval or out of nominal motor values)
initial_limits – limits for of the initial state-value
- CURRENTS = ['i_sd', 'i_sq']
List of the motor currents names
- Type:
CURRENTS(list(str))
- CURRENTS_IDX = [0, 1]
Indices for accessing all motor currents.
- Type:
CURRENTS_IDX(list(int))
- VOLTAGES = ['u_sd', 'u_sq']
List of the motor input voltages names
- Type:
VOLTAGES(list(str))
- electrical_ode(state, u_dq, omega, *_)[source]
The differential equation of the Synchronous Motor.
- Parameters:
state – The current state of the motor. [i_sd, i_sq, epsilon]
omega – The mechanical load
u_qd – The input voltages [u_sd, u_sq]
- Returns:
The derivatives of the state vector d/dt([i_sd, i_sq, epsilon])
- i_in(state)[source]
- Parameters:
state (ndarray(float)) – ODE state of the motor
- Returns:
List of all currents flowing into the motor.
- Return type:
list(float)
- property initializer
Returns: dict: Motor initial state and additional initializer parameter
- property motor_parameter
Returns: dict(float): The motors parameter dictionary
- reset(state_space, state_positions, **__)[source]
Reset the motors state to a new initial state. (Default 0)
- Parameters:
state_space (gymnasium.Box) – normalized state space boundaries
state_positions (dict) – indexes of system states
- Returns:
The initial motor states.
- Return type:
numpy.ndarray(float)
Synchronous Reluctance Motor
- class gym_electric_motor.physical_systems.electric_motors.SynchronousReluctanceMotor(motor_parameter=None, nominal_values=None, limit_values=None, motor_initializer=None)[source]
Motor Parameter
Unit
Default Value
Description
r_s
Ohm
0.57
Stator resistance
l_d
H
10.1e-3
Direct axis inductance
l_q
H
4.1e-3
Quadrature axis inductance
p
1
4
Pole pair number
j_rotor
kg/m^2
0.8e-3
Moment of inertia of the rotor
Motor Currents
Unit
Description
i_sd
A
Direct axis current
i_sq
A
Quadrature axis current
i_a
A
Current through branch a
i_b
A
Current through branch b
i_c
A
Current through branch c
i_alpha
A
Current in alpha axis
i_beta
A
Current in beta axis
Motor Voltages
Unit
Description
u_sd
V
Direct axis voltage
u_sq
V
Quadrature axis voltage
u_a
V
Voltage through branch a
u_b
V
Voltage through branch b
u_c
V
Voltage through branch c
u_alpha
V
Voltage in alpha axis
u_beta
V
Voltage in beta axis
Limits /
Nominal Value Dictionary Entries:
Entry
Description
i
General current limit / nominal value
i_a
Current in phase a
i_b
Current in phase b
i_c
Current in phase c
i_alpha
Current in alpha axis
i_beta
Current in beta axis
i_sd
Current in direct axis
i_sq
Current in quadrature axis
omega
Mechanical angular Velocity
epsilon
Electrical rotational angle
torque
Motor generated torque
u_a
Voltage in phase a
u_b
Voltage in phase b
u_c
Voltage in phase c
u_alpha
Voltage in alpha axis
u_beta
Voltage in beta axis
u_sd
Voltage in direct axis
u_sq
Voltage in quadrature axis
Note: The voltage limits should be the peak-to-peak value of the phase voltage (\(\hat{u}_S\)). A phase voltage denotes the potential difference from a line to the neutral point in contrast to the line voltage between two lines. Typically the root mean square (RMS) value for the line voltage (\(U_L\)) is given as \(\hat{u}_S=\sqrt{2/3}~U_L\)
The current limits should be the peak-to-peak value of the phase current (\(\hat{i}_S\)). Typically the RMS value for the phase current (\(I_S\)) is given as \(\hat{i}_S = \sqrt{2}~I_S\)
If not specified, nominal values are equal to their corresponding limit values. Furthermore, if specific limits/nominal values (e.g. i_a) are not specified they are inferred from the general limits/nominal values (e.g. i)
- Parameters:
motor_parameter – Motor parameter dictionary. Contents specified for each motor.
nominal_values – Nominal values for the motor quantities.
limit_values – Limits for the motor quantities.
motor_initializer –
Initial motor states (currents) (‘constant’, ‘uniform’, ‘gaussian’ sampled from
given interval or out of nominal motor values)
initial_limits – limits for of the initial state-value
- HAS_JACOBIAN = True
Parameter indicating if the class is implementing the optional jacobian function
- electrical_jacobian(state, u_in, omega, *_)[source]
Calculation of the jacobian of each motor ODE for the given inputs / The motors ODE-System.
Overriding this method is optional for each subclass. If it is overridden, the parameter HAS_JACOBIAN must also be set to True. Otherwise, the jacobian will not be called.
- Parameters:
state (ndarray(float)) – The motors state.
u_in (list(float)) – The motors input voltages.
omega (float) – Angular velocity of the motor
- Returns:
[0]: Derivatives of all electrical motor states over all electrical motor states shape:(states x states) [1]: Derivatives of all electrical motor states over omega shape:(states,) [2]: Derivative of Torque over all motor states shape:(states,)
- Return type:
Tuple(ndarray, ndarray, ndarray)
Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor
The PMSM is a three phase motor with a permanent magnet in the rotor as shown in the figure [Boecker2018b]. The input of this motor are the voltages \(u_a\), \(u_b\) and \(u_c\).
The quantities are:
\(u_a\), \(u_b\), \(u_c\) phase voltages
\(i_a\), \(i_b\), \(i_c\) phase currents
\(R_s\) stator resistance
\(L_d\) d-axis inductance
\(L_q\) q-axis inductance
\(i_{sd}\) d-axis current
\(i_{sq}\) q-axis current
\(u_{sd}\) d-axis voltage
\(u_{sq}\) q-axis voltage
\(p\) pole pair number
\(\mathit{\Psi}_p\) permanent linked rotor flux
\(\epsilon\) rotor position angle
\(\omega\) (electrical) angular velocity
\(\omega_{me}\) mechanical angular velocity
\(T\) Torque produced by the motor
\(T_L\) Torque from the load
\(J\) moment of inertia
The electrical angular velocity and the mechanical angular velocity are related such that \(\omega=\omega_{me} p\).
The circuit diagram of the phases are similar to each other and the armature circuit of the externally excited motor.
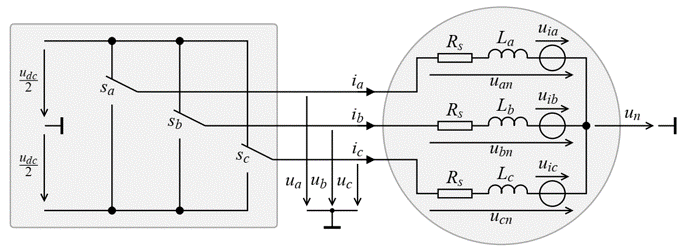
For an easy computation the three phases are first transformed to the quantities \(\alpha\) and \(\beta\) and afterwards to \(d/q\) coordinates that rotated with the rotor as given in [Boecker2018b].
This results in the equations:
\(u_{sd}=R_s i_{sd}+L_d \frac{\mathrm{d} i_{sd}}{\mathrm{d} t}-\omega_{me}p L_q i_{sq}\)
\(u_{sq}=R_s i_{sq}+L_q \frac{\mathrm{d} i_{sq}}{\mathrm{d} t}+\omega_{me}p L_d i_{sd}+\omega_{me}p \mathit{\Psi}_p\)
\(\frac{\mathrm{d} \omega_{me}}{\mathrm{d} t}=\frac{T-T_L(\omega_{me})}{J}\)
\(T=\frac{3}{2} p (\mathit{\Psi}_p +(L_d-L_q)i_{sd}) i_{sq}\)
A more detailed derivation can be found in [Modeling and High-Performance Control of Electric Machines, John Chiasson (2005)]
The difference between rms and peak values and between line and phase quantities has to be considered at the PMSM. The PMSM is in star conncetion and the line voltage \(U_L\) is mostly given in data sheets as rms value. In the toolbox the nominal value of the phase voltage \(\hat{U}_S=\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}}U_L\) is needed. Furthermore, the supply voltage is typically the same \(u_{sup}=\hat{U}_S\). For example, a line voltage of \(U_L=400~\text{V}\) is given, the rms phase voltage is \(U_S=\sqrt{\frac{1}{3}}U_L = 230.9 \text{ V}\) and the peak value \(\hat{U}_S=326.6 \text{ V}\). The nominal peak current of a phase is given by \(\hat{I}_S=\sqrt{2} I_S\).
- class gym_electric_motor.physical_systems.electric_motors.PermanentMagnetSynchronousMotor(motor_parameter=None, nominal_values=None, limit_values=None, motor_initializer=None)[source]
Motor Parameter
Unit
Default Value
Description
r_s
Ohm
18e-3
Stator resistance
l_d
H
0.37e-3
Direct axis inductance
l_q
H
1.2e-3
Quadrature axis inductance
p
1
3
Pole pair number
j_rotor
kg/m^2
0.03883
Moment of inertia of the rotor
Motor Currents
Unit
Description
i_sd
A
Direct axis current
i_sq
A
Quadrature axis current
i_a
A
Current through line a
i_b
A
Current through line b
i_c
A
Current through line c
i_alpha
A
Current in alpha axis
i_beta
A
Current in beta axis
Motor Voltages
Unit
Description
u_sd
V
Direct axis voltage
u_sq
V
Quadrature axis voltage
u_a
V
Phase voltage for line a
u_b
V
Phase voltage for line b
u_c
V
Phase voltage for line c
u_alpha
V
Phase voltage in alpha axis
u_beta
V
Phase voltage in beta axis
Limits /
Nominal Value Dictionary Entries:
Entry
Description
i
General current limit / nominal value
i_a
Current in phase a
i_b
Current in phase b
i_c
Current in phase c
i_alpha
Current in alpha axis
i_beta
Current in beta axis
i_sd
Current in direct axis
i_sq
Current in quadrature axis
omega
Mechanical angular Velocity
torque
Motor generated torque
epsilon
Electrical rotational angle
u_a
Phase voltage in phase a
u_b
Phase voltage in phase b
u_c
Phase voltage in phase c
u_alpha
Phase voltage in alpha axis
u_beta
Phase voltage in beta axis
u_sd
Phase voltage in direct axis
u_sq
Phase voltage in quadrature axis
Note
The voltage limits should be the peak-to-peak value of the phase voltage (\(\hat{u}_S\)). A phase voltage denotes the potential difference from a line to the neutral point in contrast to the line voltage between two lines. Typically the RMS value for the line voltage (\(U_L\)) is given as \(\hat{u}_S=\sqrt{2/3}~U_L\)
The current limits should be the peak-to-peak value of the phase current (\(\hat{i}_S\)). Typically the RMS value for the phase current (\(I_S\)) is given as \(\hat{i}_S = \sqrt{2}~I_S\)
If not specified, nominal values are equal to their corresponding limit values. Furthermore, if specific limits/nominal values (e.g. i_a) are not specified they are inferred from the general limits/nominal values (e.g. i)
- Parameters:
motor_parameter – Motor parameter dictionary. Contents specified for each motor.
nominal_values – Nominal values for the motor quantities.
limit_values – Limits for the motor quantities.
motor_initializer –
Initial motor states (currents) (‘constant’, ‘uniform’, ‘gaussian’ sampled from
given interval or out of nominal motor values)
initial_limits – limits for of the initial state-value
- HAS_JACOBIAN = True
Parameter indicating if the class is implementing the optional jacobian function
- electrical_jacobian(state, u_in, omega, *args)[source]
Calculation of the jacobian of each motor ODE for the given inputs / The motors ODE-System.
Overriding this method is optional for each subclass. If it is overridden, the parameter HAS_JACOBIAN must also be set to True. Otherwise, the jacobian will not be called.
- Parameters:
state (ndarray(float)) – The motors state.
u_in (list(float)) – The motors input voltages.
omega (float) – Angular velocity of the motor
- Returns:
[0]: Derivatives of all electrical motor states over all electrical motor states shape:(states x states) [1]: Derivatives of all electrical motor states over omega shape:(states,) [2]: Derivative of Torque over all motor states shape:(states,)
- Return type:
Tuple(ndarray, ndarray, ndarray)